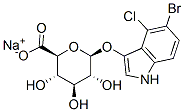
Description
Chromogenic substrate for beta-glucuronidase (GUS) yielding a blue precipitate upon cleavage. Used for identification of beta-glucuronidase. X-beta-D-glucuronide has been reported as chromogenic substrate in a number of chromogenic E. coli / coliform culture media. About 95% of common E. coli possess beta-D-glucuronidase activity. Such chromogenic culture media are used for detection and enumeration of E. coli in food samples such as meat, dairy products, shellfish and have clinical applications in the assessment of urinary infections. It has gained international acceptance as highly accurate test for the presence of E. coli in drinking water samples. It is also used for the detection of the expression of GUS (E. coli beta-glucuronidase) gene fusion marker constructs in plants. The sodium salt has advantages over the cyclohexylammonium salt as being nonelectrostatic and possessing a naturally-occurring cation. 1. Bauer R., Paltauf F., Kohlwein S.D., Functional expression of bacterial beta-glucuronidase and its use as a reporter system in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Yeast 1993, 9, 71-5. 2. Daniell H., Foreign gene expression in chloroplasts of higher plants mediated by Tungsten particle bombardment. Methods Enzymol. 1993, , 536. 3. Jefferson R.A., Kavanagh T.A., Bevan M.W., GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3901-7. 4. Okrend A.J., et al., Use of 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indoxyl-beta-D-glucuronide in MacConkey sorbitol agar to aid in the isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from ground beef. J. Food Protect. 1990, 53, 941. 5. Restaino L., Frampton E.W., Blaszko N., Evaluation of the beta-glucuronidase substrate 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-beta-D-glucuronide (X-GLUC) in a 24-hour direct plating method for Escherichia coli. J. Food Protect. 1988, 51, 402. 6. Restaino L., Frampton E.W., Lyon R.H., Use of the chromogenic substrate 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-beta-D-glucuronide (X-GLUC) for enumerating Escherichia coli in 24 h from ground beef. J. Food Protect. 1990, 53, 508. 7. Turner K.M., Restaino L., Frampton E.W., Efficacy of chromocult agar for coliform and Escherichia coli detection in foods. J. Food Protect. 2000, 63, 539-41. 8. Watkins W.D., Rippey S.R., Clavet C.R., Kelley-Reitz D.J., Burkhardt W. 3rd., Novel compound for identifying Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 1874-5.


 Chemical-Suppliers.eu
Chemical-Suppliers.eu